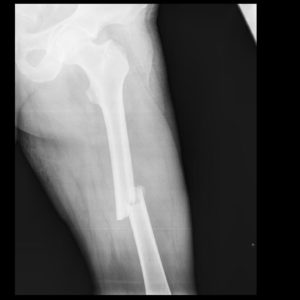
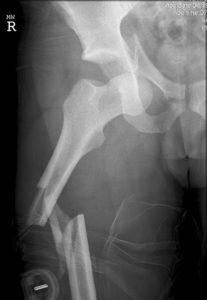
Fracture is the orthopaedic terminology to describe a broken bone. These are usually the result of direct trauma to the body or extremity. These injuries can be treated with surgery or without. Nonoperative treatment usually entails a cast or brace of some time to immobilize the extremity involved. Surgery usually involves the use of an implant to hold the bone in its anatomic position. This is also referred to as internal fixation.
Types of Fractures
Click on the topics below to read more about them on the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons website.
- Distal Humerus Fractures of the Elbow
- Elbow (Olecranon) Fractures
- Elbow Fractures in Children
- Scapula (Shoulder Blade) Fractures
- Shoulder Trauma (Fractures and Dislocations)
- Femur Shaft Fractures (Broken Thighbone)
- Fracture of the Pelvis
- Hip Fractures
- Pediatric Thighbone (Femur) Fracture
- Distal Femur (Thighbone) Fractures of the Knee
- Growth Plate Fractures
- Stress Fractures
- Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures
- Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle)
- Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
- Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury
- Pilon Fractures of the Ankle
- Sprained Ankle
- Stress Fractures of the Foot and Ankle
- Talus Fractures
- Toe and Forefoot Fractures
- Fractures (Broken Bones)
- Open Fractures
- Helping Fractures Heal (Orthobiologics)
- Internal Fixation for Fractures